Strategies for Finding New Equity Capital
[ad_1]
Financial Management
- ABC plc has grown from a company with £10,000 turnover to one with a £17m turnover and £1.8m profit in the last five years. The existing owners have put all their financial resources into the firm to enable it to grow. The directors wish to take advantage of a very exciting market opportunity but would need to find £20m of new equity capital as the balance sheet is already over-geared (i.e. has high debt). The options being discussed, in a rather uniformed way, are flotation on the Main Market of the London Stock Exchange, a flotation on the Alternative Investment Market and private equity. Write a report to enlighten the board on the merits and disadvantages of each of these three possibilities.
Answer:
Option 1 – Floatation on the main market of LSE.
Floating money from LSE will lead to listing of shares of the company. Demerits of listing shares on stock exchange will lead to increase in legal compliances, which will also increase the cost of the company. As the company has grown drastically during the past 5 years, it will be easy for raising money from market which will form part of merits of floating money from LSE. Risks will be shared and a new debt will not appear in balance sheet of the Company. On the other hand raising funds through stock market would lead to loss of ownership and control over the company.
Option 2 – Private Equity
Private equity is raising money from handful of investors. Merits of raising funds through private equity are – large amount of funds can be raised , the investors also be a part of management due to which the business is monitored closely by a third party, huge returns can be obtained from private equity investments.
Some of the demerits of private equity are loss of management control and dilution of ownership in the Company.
Option 3 –
Alternative Investment Market is getting investment form alternate sources. (Andrew Killick Head of Corporate Finance (South Region) – Baker Tilly)
Merits – The regulations for raising money from Alternative Investment Market are lighter hence it saves the corporate expense. The paying of merger and acquisition is easier.
Demerits – There is loss of control as the institutions (investors) own large share in the company. Floatation puts the company in the spotlight and under scrutiny, and this continues throughout a public company’s life which reduces the privacy. The company has to report results to a tighter timetable and to International Financial Reporting Standards.
Management Accounting
Management accounting team also come up with some questions and request you to explain/answer them for upcoming board meeting:
- What is the point of distinguishing between absorption and marginal costing? Why they report different profit, explain with an example?
Answer:
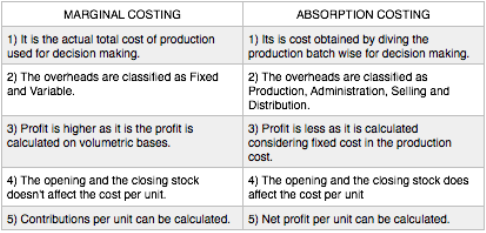
Example :
Variable cost of a product x – 10 p.u, fixed cost for the period – 100000, Number of units produced – 10000, closing stock – 1000 units, material cost – 15 p.u
Value of closing stock under both methods-
Marginal costing
Closing stock = (Material cost+Variable cost) * Number of Units
= (15+10)*1000 = 25000
Absorption Costing
Closing stock = Total cost throughout the year/ total units produced * closing stock
= 100000 (fixed cost)+ 100000 (variable cost) + 150000 (material cost)/ 10000*1000
=350000/10000*1000
=35000
- The management of XYZ company is concerned about the its inability to obtain enough fully trained labour to enable it to meet its present budget projection:
|
Service |
A |
B |
C |
Total |
|
Variable costs |
||||
|
Materials |
8 |
6 |
7 |
21 |
|
Labour |
11 |
8 |
14 |
33 |
|
Expenses |
5 |
4 |
4 |
13 |
|
Allocated fixed cost |
6 |
15 |
12 |
33 |
|
Total cost |
30 |
33 |
37 |
82 |
|
Profit |
17 |
4 |
4 |
25 |
|
Sales revenue |
47 |
37 |
41 |
107 |
The amount of labour likely to be available amounts to £23,000. All of the variable labour is paid at the same hourly rate. You are asked to prepare a statement of plans, ensuring that at least 50 per cent of the budgeted sales revenues are achieved for each service and the balance of labour is used to produce the greater profit.
- What steps could the business take in an attempt to improve profitability, in the light of the labour shortage?ANSWER
To improve the profit in the light of labour, company should B is the most profited company as it has the maximum profit per unit labour. The second preference should be given to company A as it provides better profit per unit labour then company C. And company C is the last option with least profit per unit labour.
- M&M plc makes Product E, the standard costs of which are:
|
Sales Revenue |
£40 |
|
Direct labour (1 hour) |
(13) |
|
Direct materials (1 kg) |
(12) |
|
Fixed overheads |
(5) |
|
Standard profit |
10 |
The budgeted output for March was 1,000 units of Product E; the actual output was 1,100 units, which was sold for £44,400. There were no inventories at the start or end of March.
The actual production costs were:
Direct labour (1,075 hours)£14,513
Direct Materials (1,170 kg)13,455
Fixed overheads 5,700
How flexible budget will help this company to identify the budget variance?
ANSWER
Flexible Budget – Flexible budget calculates expenditure levels for variable costs. Depending upon the actual revenue different variable cost are considered. Flexible budget results in varying budget depending upon the activities performed.
In this case the actual revenue of the company has exceeded the budgeted revenue. The factors affecting the actual revenue and budgeted revenue are Sales, Material, Fixed Overhead, Profit, Labour. So the difference between the actual and budgeted revenue can be easily calculated using Flexible budgeting.
REFERENCES
- Andrew Killick Head of Corporate Finance (South Region) – Baker Tilly)
The post Strategies for Finding New Equity Capital appeared first on mynursinghomeworks.
[ad_2]
Source link

